Biomass production needs to become sustainable
Biomass is a form of renewable energy that derives from living, or recently living organisms. The most common source of biomass is wood. Wood has been used since the ancient times, mostly to produce fire needed for heating and cooking purposes.
What makes biomass a form of renewable energy? Biomass is a renewable energy source because the plants can be re-grown time and time again, and in a relatively short period of time. With smart exploitation biomass can be continuous energy source – only thing here is to adjust biomass production capabilities with biomass exploitation rate.
Biomass is today one of the major renewable energy sources, together with hydropower and wind energy. Biomass has one very important advantage over other renewable energy sources, namely it can be produced almost everywhere on this planet. In fact, many renewable energy studies look at biomass as one of the top future energy sources, a one on which clean energy economy can be built upon.
The generally accepted opinion about biomass is that this is a carbon neutral source, meaning that it produces far less damage to climate change as compared to currently dominant fossil fuels, though this theory also had certain studies which disagree with this thesis, and believe that unsustainable biomass production could in fact lead to even bigger damage to our climate than sticking with coal, oil and natural gas. Main reason here is fact that fossil fuels are inactive component in nature and with their exploitation there is no biological “hole” created in nature, as is with deforestation. Because of that it is of vital importance that biomass sources are managed with great care and harvested sustainably, or otherwise increased biomass production can cause a great damage to our environment.
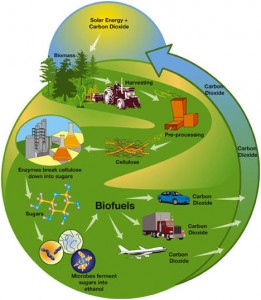
The sustainable biomass production is something that can be done with proper management. This includes adequate precautionary measures as well as various procedures that would result in minimal environmental damage. Our society also has to make sure not to turn much of our agricultural land into energy crops because biomass production mustn’t compete with food crops for the land, at least not when there are so many hungry people in the world.
The possible solution for this issue include using biomass sources such as wheat straw and corn stover residues, forest residues and sustainably-harvested woods, as well as clean industrial and municipal wastes.
The basic principle of any future biomass production should be that the emissions of biomass carbon are completely recycled by future plant growth within a comparatively short period of time. That way, biomass wouldn’t contribute to further increase of greenhouse gas emissions.
In U.S. biomass currently accounts for approximately 50 billion kilowatt hours of electricity per year, meaning it’s placed third among renewable energy sources, behind hydropower and wind energy.
The further advancement in technologies for biomass production can no doubt significantly increase total share of biomass in U.S. energy mix. There are however certain factors that mustn’t be overlooked such as land use and harvesting practices, availability of resources and amount of fuel needed for transportation, and most important its carbon footprint. Only sustainable biomass production is acceptable future energy solution.



